AI-based orchestration for cloud-native ultra low latency applications
Gent | More than two weeks ago
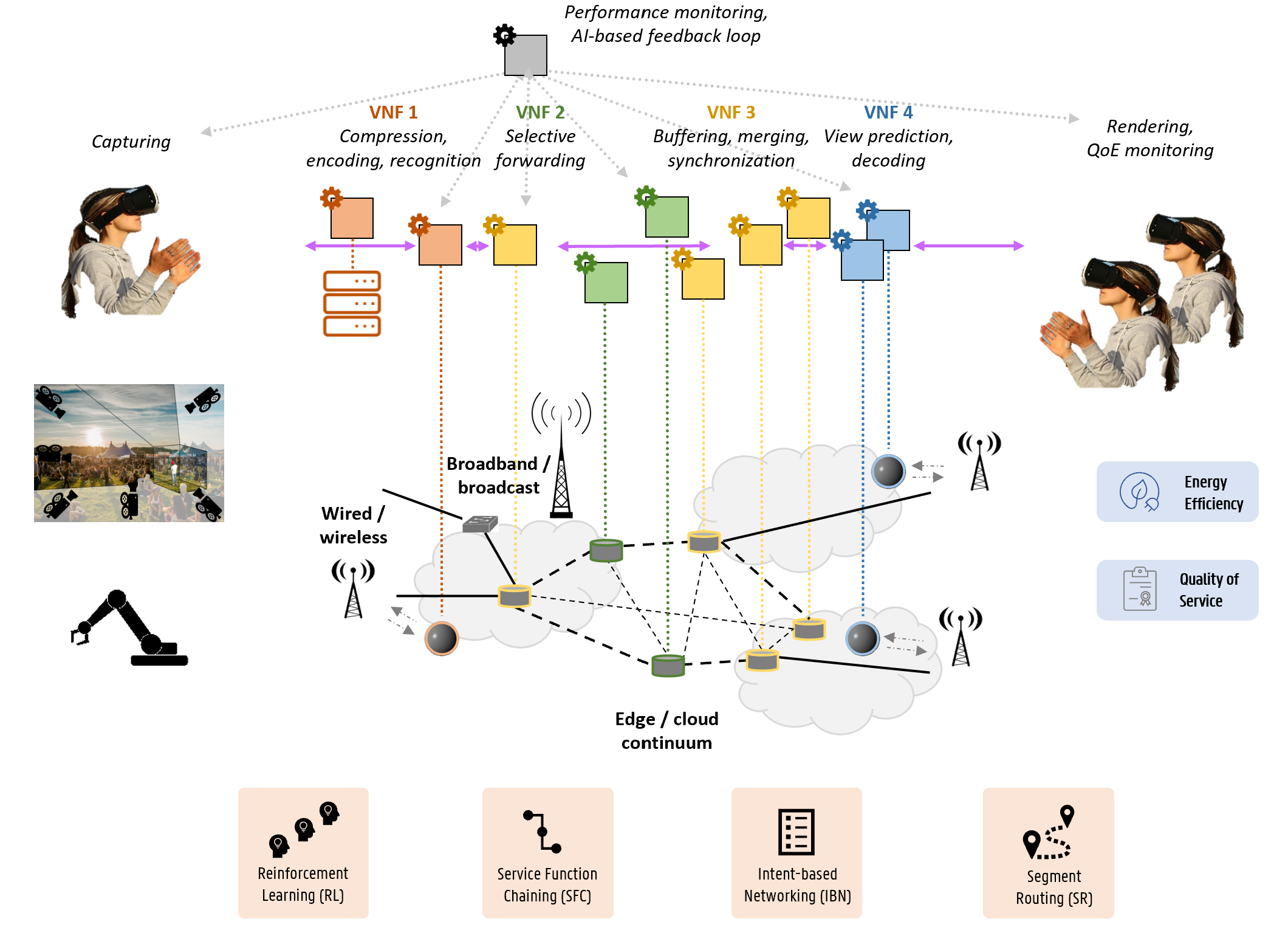
Applications that rely on remote communication, collaboration and sensing are becoming more and more distributed over large networks and are demanding increasing amounts of computational and networking resources. Next-generation services in eHealth, immersive telepresence, automotive, retail and industry all deal with ultra-low latency and high-throughput requirements that cannot be met by monolithic deployments. Such applications are instantiated as Service Function Chains (SFC), involving multiple multi-tenant components that are often AI-based themselves.
Potential breakthroughs at the network level include novel paradigms for higher flexibility, precision and scalability, such as Deterministic Networking (DetNet), Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and Segment Routing (SR), each with their own latency-aware design features. In addition, Intent-based Networking (IBN) holds promises to enforce networking rules without relying on explicit system details.
Efficient orchestration strategies for computational resources are primordial to complement the network management solutions and provide efficient and high-throughput data processing. Highly dynamic, AI-based micro-service provisioning is required to circumvent current resource fragmentation problems among multiple network and service providers and reduce execution times along the end-to-end path of the service chain, while ensuring reliability, scalability, security and energy-efficiency.
Many of these networking and orchestration solutions remain largely unexplored, especially on their interactions and control loops in cloud-native environments that span multiple domains. Integrating Deep Learning (DL) methods in orchestration practices and designing Reinforcement Learning (RL) systems capable of performing service scheduling are among the major research challenges in the network and cloud management domain.
This position will place special emphasis on:
- Energy-efficiency and sustainability as a primary orchestration objective, addressing one of the most pressing challenges in the domain.
- Digital Twins as a means to model, simulate, and validate orchestration strategies before real-world deployment.
- Multi-objective optimization strategies, balancing latency, throughput, energy consumption, cost, among others.
Expected Outcomes include:
Design and implementation of prototypes of AI-driven orchestration systems.
Development of benchmarks and open datasets for reproducible evaluation.
- Integration and validation within existing cloud-native platforms such as Kubernetes.
Required background: Computer Science, Computer Science Engineering, Information Engineering Technology, Electrical Engineering, Applied Physics, ICT and electronics
Type of work: 60% modeling/algorithms design/simulation, 20% experimental, 10% literature
Supervisor: Filip De Turck
Co-supervisor: Tanguy Coenen
Daily advisor: Tim Wauters
The reference code for this position is 2026-080. Mention this reference code on your application form.
